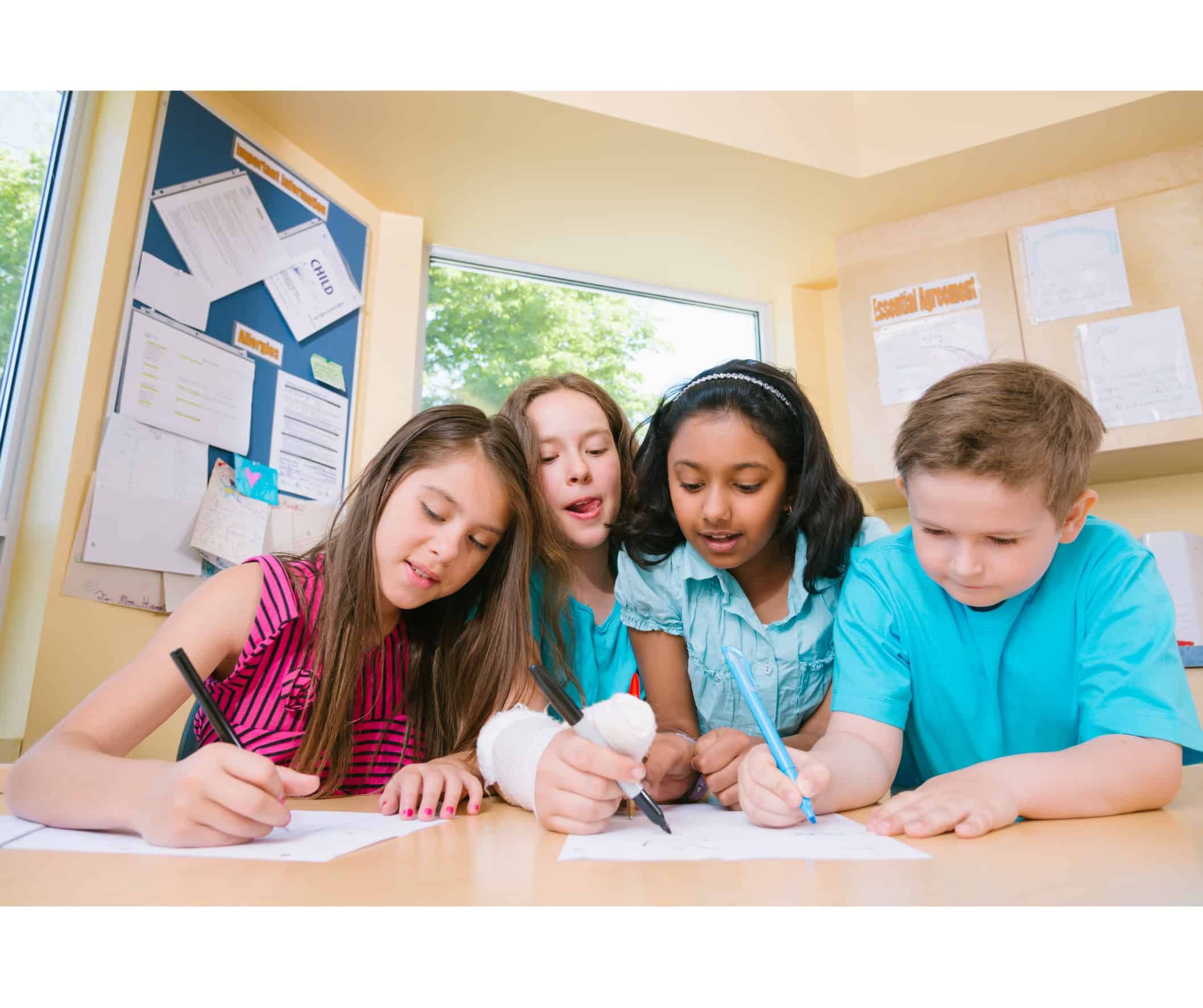
Self and Peer-Correction Techniques in Teaching
Researchers conducted an updated review of the literature on interventions to promote overall self-determination and skills associated with self-determined action in students with disabilities in the school context.
14 Apr 2024